Navigation Menu
Contact Us
- Email:
- info@wxavatar.com
- Address:
- Yurong Village, Yuqi Street, Huishan District, Wuxi, China.
Release Date:May 20, 2025 Visit:64 Source:Roll Forming Machine Factory
In the metal fabrication industry, efficiency and precision are key factors that determine productivity and product quality. Door angle roll forming lines have emerged as specialized equipment designed to address specific manufacturing needs. This article explores how these systems function and their potential impact on fabrication processes.
Understanding Door Angle Roll Forming Technology
Door angle roll forming lines are specialized machines that continuously shape metal coils into precise angular profiles used primarily in door frame construction. These systems utilize a series of rollers that gradually bend the metal stock into the desired cross-section without removing material, distinguishing them from other metal shaping methods.
The process begins with decoiling, where metal coils are fed into the system. The material then passes through multiple roller stations, each performing incremental bends until achieving the final angle profile. This continuous operation allows for consistent production of long lengths with uniform dimensions.
Operational Advantages in Production Environments
One notable aspect of door angle roll forming lines is their ability to maintain consistent product quality throughout production runs. The mechanized process minimizes human error potential that can occur with manual bending operations. This consistency becomes particularly valuable when manufacturing components that require precise dimensional tolerances for proper door assembly and function.
These systems also demonstrate adaptability to various production scales. While offering advantages for larger volume operations, they can also be configured for smaller batch production when needed. The setup can accommodate different metal thicknesses and material types, providing flexibility for manufacturers working with diverse project requirements.
Production Capacity Considerations
When properly configured and maintained, door angle roll forming equipment can contribute to enhanced output capabilities. The continuous nature of the forming process often allows for faster production compared to some alternative methods. Many systems incorporate automated features that reduce manual handling requirements, allowing operators to focus on quality control and process monitoring.
Modern implementations often include computerized controls that enable precise adjustment of forming parameters. This level of control helps maintain product consistency while allowing for quick changeovers between different profile specifications. Some advanced models feature real-time monitoring systems that can track production metrics and identify potential issues early in the process.
Maintenance and Long-Term Performance
The durability of door angle roll forming lines depends on proper maintenance practices and operating conditions. Regular inspection of roller surfaces, alignment checks, and lubrication of moving components help preserve equipment performance over time. Many manufacturers provide detailed maintenance schedules and operational guidelines to support optimal equipment lifespan.
Training for operators plays a significant role in maximizing the benefits of these systems. Understanding proper setup procedures, troubleshooting techniques, and safety protocols contributes to both equipment longevity and production efficiency. Some suppliers offer comprehensive training programs alongside equipment installation to ensure proper operation from the outset.
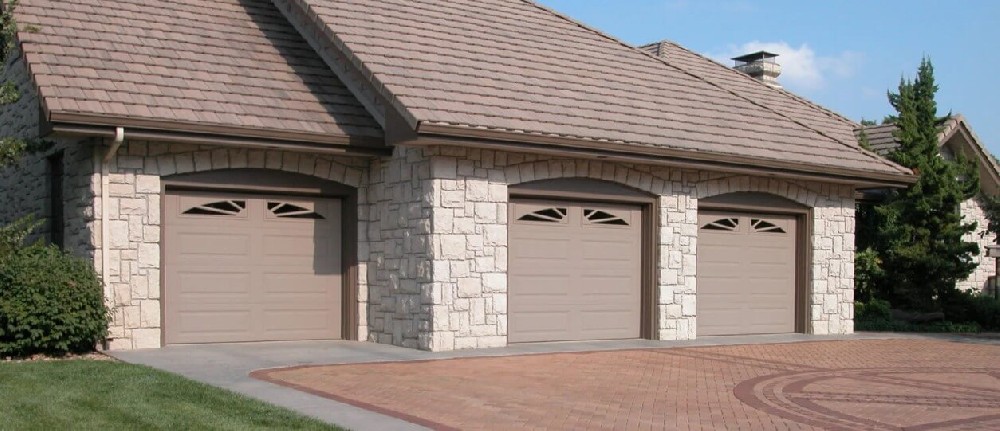

Conclusion
Door angle roll forming lines represent a specialized solution for metal fabricators producing angular profiles for door applications. Their design focuses on creating consistent, precise components while offering production flexibility. As with any industrial equipment, realizing the full potential of these systems requires proper selection, operation, and maintenance tailored to specific manufacturing requirements. For operations regularly producing door frame components, these forming lines can offer measurable improvements in product consistency and production workflow.