Navigation Menu
Contact Us
- Email:
- info@wxavatar.com
- Address:
- Yurong Village, Yuqi Street, Huishan District, Wuxi, China.
Release Date:May 12, 2025 Visit:62 Source:Roll Forming Machine Factory
Roll forming machine is a common metal processing equipment, widely used in construction, automobile, home appliance and other industries. Its core function is to gradually bend the metal coil through multiple rollers to obtain the desired cross-sectional shape. So, what materials are the key components of this machine made of? How will the selection of different materials affect the performance and life of the machine? Let's find out together.
1. Frame: The cornerstone of stability
The frame of the roll forming machine is usually made of high-strength cast iron or welded steel structure. The cast iron frame has good shock absorption performance and can effectively absorb vibration during processing, which is suitable for high-precision forming needs. The welded steel frame is lighter and suitable for production lines that need frequent adjustment or movement. Some high-end models will also strengthen the key stress-bearing parts, such as adding ribs or using special heat treatment processes to improve overall rigidity.
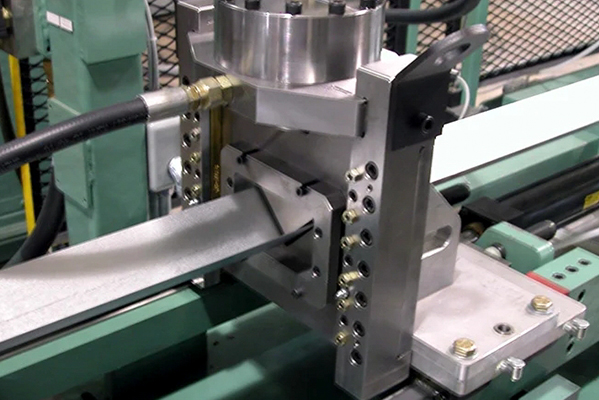
2. Roller: Balance of wear resistance and precision
The roller is in direct contact with the metal sheet, and its material selection is crucial. Common roller materials include:
Alloy tool steel: such as Cr12MoV, SKD11, etc. After quenching and tempering, the hardness can reach HRC58-62, which is suitable for long-term high-load operation.
High-speed steel: Excellent performance in high-speed continuous forming, stronger wear resistance, but higher cost.
Surface hardened steel: Through carburizing or nitriding treatment, the surface is hardened while the inside remains tough, suitable for working conditions with large impact.
In order to further improve the life, some rollers will be chrome-plated or sprayed with tungsten carbide to reduce the wear caused by metal friction.
3. Transmission components: the key to power transmission
The transmission system of the roll forming machine usually includes gears, chains, bearings and other components. The material selection of these components directly affects the operating efficiency of the equipment:
Gears: Alloy steels such as 20CrMnTi are mostly used, and carburizing and quenching are performed to increase the hardness of the tooth surface.
Bearings: High-precision bearing steel (such as GCr15) is the mainstream choice, and some heavy equipment will use ceramic hybrid bearings to reduce friction.
Drive shaft: Medium carbon alloy steels such as 40Cr or 42CrMo are tempered to ensure sufficient strength and toughness.
4. Auxiliary components: Details determine the experience
In addition to the core components, the auxiliary components of the roll forming machine are also worth paying attention to:
Guide device: usually made of wear-resistant copper alloy or polymer materials to reduce direct friction between metals.
Lubrication system: Copper or stainless steel oil pipes are combined with high-viscosity industrial lubricants to ensure long-term stable operation.
Electrical components: Metal housings and wear-resistant cables with high protection levels are adapted to workshop environments.
5. Practical considerations for material selection
Different industries have different requirements for roll forming machines, for example:
The construction industry pays more attention to the stability and large load capacity of the equipment, so the frame and rollers tend to be heavy.
Home appliances or precision manufacturing industries may pay more attention to forming accuracy and use higher-grade alloy steel and precision bearings.
In addition, maintenance cost is also an important factor. For example, although some wear-resistant coatings have a high initial investment, they can greatly reduce the frequency of replacement, which is more economical in the long run.

Conclusion
The material selection of the roll forming machine is not fixed, but needs to be weighed according to the specific purpose, production environment and cost budget. Understanding the characteristics of these materials can not only help users better choose equipment, but also more reasonably maintain and maintain it in daily use to extend the service life of the machine. The next time you see the roll forming machine in operation, you may have a better understanding of the material knowledge hidden behind the steel.