Navigation Menu
Contact Us
- Email:
- info@wxavatar.com
- Address:
- Yurong Village, Yuqi Street, Huishan District, Wuxi, China.
Release Date:Apr 29, 2025 Visit:73 Source:Roll Forming Machine Factory
The rolling process is a fundamental metalworking technique used to shape and refine metal materials by passing them through one or more pairs of rolls. This method plays a crucial role in manufacturing, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility in producing various metal products. Below, we explore the key purposes and advantages of the rolling process.
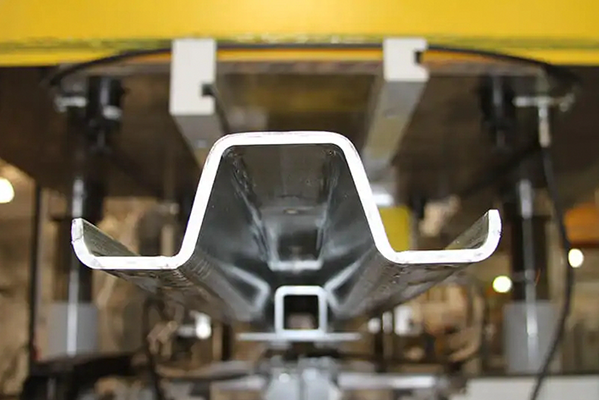
1. Shaping and Forming Metal
One of the primary purposes of rolling is to reduce the thickness of metal workpieces while increasing their length or width. By applying compressive forces, the process transforms raw metal ingots, slabs, or billets into sheets, plates, bars, or structural shapes like I-beams and rails.
Hot Rolling is performed at high temperatures, making the metal more malleable and suitable for large-scale deformation.
Cold Rolling occurs at or near room temperature, enhancing surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
2. Improving Material Properties
The rolling process enhances the mechanical properties of metals through grain refinement and work hardening. Cold rolling, in particular, increases strength and hardness while maintaining ductility to a certain extent. Additionally, controlled rolling can optimize microstructure for better performance in specific applications.
3. Achieving Precise Dimensions and Surface Quality
Rolling ensures consistent thickness and smooth surfaces, which are essential for industries requiring high precision, such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Advanced rolling mills can produce ultra-thin foils and coated sheets with tight tolerances.
4. Enhancing Production Efficiency
Compared to other metal-forming methods, rolling is a continuous and high-speed process, making it cost-effective for mass production. Modern automated rolling mills minimize material waste and reduce labor requirements, contributing to overall manufacturing efficiency.
5. Enabling Diverse Industrial Applications
Rolled metal products serve a wide range of industries:
Construction: Structural steel beams, reinforcement bars
Transportation: Automotive body panels, aircraft components
Consumer Goods: Appliances, packaging materials
Energy: Pipelines, electrical conductors
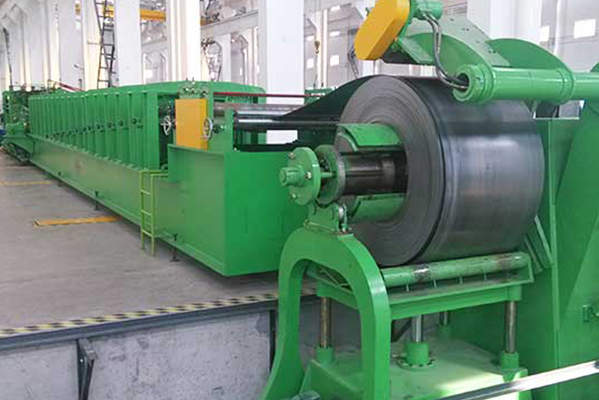

Conclusion
The rolling process is indispensable in modern manufacturing, offering precise shaping, improved material characteristics, and high production efficiency. Its adaptability across various industries underscores its importance in producing high-quality metal products that meet diverse industrial demands.
By understanding the purpose and benefits of rolling, manufacturers can optimize their production processes to deliver reliable and high-performance metal components.