Navigation Menu
Contact Us
- Email:
- info@wxavatar.com
- Address:
- Yurong Village, Yuqi Street, Huishan District, Wuxi, China.
Release Date:Jun 25, 2025 Visit:71 Source:Roll Forming Machine Factory
The lighting manufacturing industry faces numerous challenges when producing high-speed lighting products. As demand grows for efficient and reliable lighting solutions, manufacturers must navigate complex technical, operational, and market-related obstacles. This article explores the primary challenges in high-speed lighting production and how industry leaders address them.
1. Precision in Component Assembly
High-speed lighting production requires extreme precision in assembling small, delicate components. LED chips, drivers, and heat sinks must be positioned accurately to ensure optimal performance. Even minor misalignments can lead to product failures, increasing waste and reducing efficiency. Automated assembly systems help mitigate these issues, but maintaining consistent precision at high speeds remains a persistent challenge.
2. Thermal Management Optimization
Excessive heat negatively impacts lighting performance and longevity. In high-speed production, ensuring proper thermal dissipation without slowing down manufacturing is difficult. Manufacturers must balance rapid assembly with effective heat sink integration and thermal paste application. Advanced materials and automated thermal testing systems help maintain quality while keeping production speeds high.
3. Supply Chain and Material Consistency
Reliable sourcing of high-quality materials is critical for consistent lighting production. Fluctuations in raw material availability, such as semiconductors and rare-earth elements, can disrupt manufacturing schedules. Suppliers must meet strict specifications to prevent defects, making supply chain management a key challenge in maintaining uninterrupted high-speed production.
4. Quality Control at High Volumes
Maintaining consistent product quality becomes increasingly difficult as production speeds rise. Defects such as flickering, color inconsistencies, or premature failure must be detected early without slowing down the assembly line. Automated optical inspection (AOI) and real-time testing systems help identify issues, but implementing these solutions without compromising efficiency requires careful optimization.
5. Rapid Technological Advancements
Lighting technology evolves quickly, with new efficiency standards and smart lighting features emerging regularly. Manufacturers must adapt production lines to accommodate these changes without excessive downtime. Retooling for new designs or materials can be costly and time-consuming, making flexibility a crucial factor in high-speed lighting production.
6. Cost Efficiency and Competitive Pricing
Balancing high-speed production with cost efficiency is essential to remain competitive. While automation reduces labor costs, initial investments in advanced machinery are significant. Manufacturers must optimize processes to minimize waste and energy consumption while maintaining high output levels.
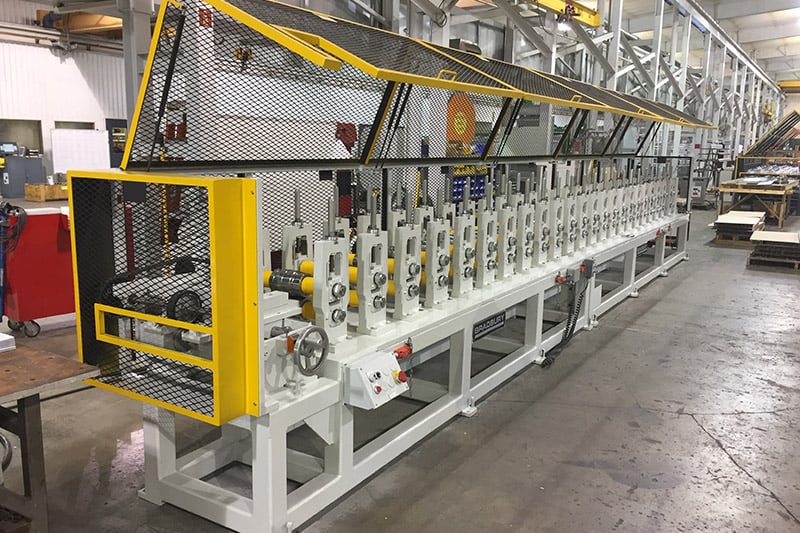

Conclusion
High-speed lighting production presents multiple challenges, from precision assembly to supply chain reliability and quality control. Manufacturers that invest in automation, advanced testing, and flexible production systems can overcome these hurdles while meeting market demands. As technology advances, continuous improvement in manufacturing processes will be key to sustaining growth in the lighting industry.