Navigation Menu
Contact Us
- Email:
- info@wxavatar.com
- Address:
- Yurong Village, Yuqi Street, Huishan District, Wuxi, China.
Release Date:Jun 25, 2025 Visit:75 Source:Roll Forming Machine Factory
The manufacturing sector is undergoing a significant transformation with the adoption of smart factory concepts. Lighting component assembly, a critical segment of the electronics industry, stands to benefit substantially from these technological advancements. Smart factories integrate advanced automation, data analytics, and interconnected systems to create more responsive and efficient production environments.
Enhanced Precision in Component Assembly
Smart factory technologies bring unprecedented precision to lighting component assembly. Computer-controlled robotic systems can handle delicate LED chips and optical components with micron-level accuracy, reducing human error in placement and soldering processes. Machine vision systems provide real-time quality inspection, identifying microscopic defects that might escape human detection. This level of precision contributes to improved product consistency and reliability in lighting components.
Data-Driven Process Optimization
The implementation of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors throughout the assembly line generates vast amounts of production data. Advanced analytics platforms process this information to identify bottlenecks, predict maintenance needs, and optimize workflow patterns. For lighting manufacturers, this means being able to fine-tune assembly parameters for different component types, adjust production schedules based on real-time demand, and minimize material waste through better inventory management.
Adaptive Manufacturing for Customization
Smart factories enable greater flexibility in lighting component production. Digital twin technology allows manufacturers to simulate and test assembly processes for new lighting designs before physical production begins. Modular production systems can quickly reconfigure to accommodate different product specifications, making it practical to offer customized lighting solutions without sacrificing efficiency. This adaptability is particularly valuable as lighting technology continues to evolve with new form factors and functionality requirements.
Workforce Transformation in Assembly Facilities
The shift to smart manufacturing changes the nature of work in lighting component assembly. While some traditional assembly roles may diminish, new positions emerge requiring skills in system monitoring, data interpretation, and robotic equipment maintenance. Training programs are helping existing workers transition to these higher-value roles, creating opportunities for career advancement within the industry.
Challenges in Implementation
Adopting smart factory technology presents several considerations for lighting component manufacturers. The initial investment in equipment and infrastructure can be substantial, requiring careful planning to ensure return on investment. Integration with existing systems may require phased implementation approaches. Additionally, the increased reliance on networked systems necessitates robust cybersecurity measures to protect intellectual property and production data.
Future Outlook for Lighting Manufacturing
As smart factory technologies mature, their application in lighting component assembly is expected to expand. Emerging developments in artificial intelligence, edge computing, and advanced materials may further enhance production capabilities. Manufacturers who embrace these technologies position themselves to meet evolving market demands with greater agility and cost-effectiveness.
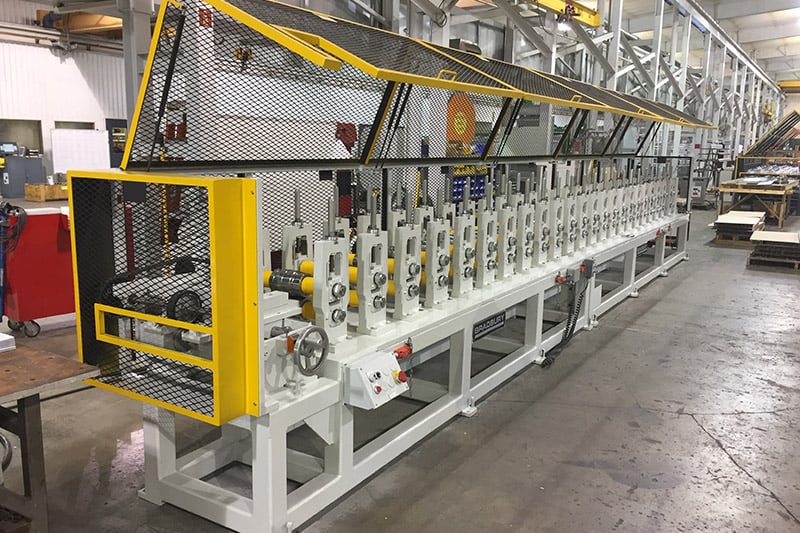

The transition to smart manufacturing represents a significant evolution in how lighting components are produced. While not without challenges, these advanced production methods offer substantial benefits in quality, efficiency, and flexibility that can strengthen the competitive position of lighting manufacturers in a dynamic global market.